Java Stream的Collectors方法适合大多数用例。它们允许返回aCollection或标量。对于前者,使用一种toXXX()方法,对于后者,使用一种方法reducing()。
让我们想象一个实现购物车的电子商务平台。该购物车的建模如下:
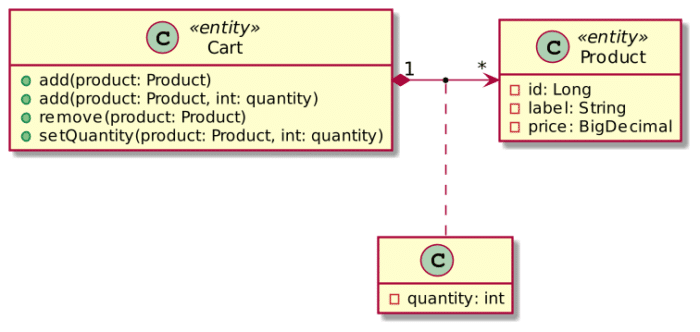
这非常类似DDD设计中聚合,Cart作为一个聚合根实体。
public class Product {
private final Long id; // 1
private final String label; // 1
private final BigDecimal price; // 1
public Product(Long id, String label, BigDecimal price) {
this.id = id;
this.label = label;
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object object ) { ... } // 2
@Override
public int hashCode() { ... } // 2
}
public class Cart {
private final Map<Product, Integer> products = new HashMap<>(); // 1
public void add(Product product) {
add(product, 1);
}
public void add(Product product, int quantity) {
products.merge(product, quantity, Integer::sum);
}
public void remove(Product product) {
products.remove(product);
}
public void setQuantity(Product product, int quantity) {
products.put(product, quantity);
}
public Map<Product, Integer> getProducts() {
return Collections.unmodifiableMap(products); // 2
}
}
|
定义了如何在内存中存储数据后,我们需要设计如何在屏幕上显示购物车。我们知道,结帐屏幕需要显示两个不同的信息位:
- 行的列表,其中每一行的价格,即每种产品的价格乘以数量。
- 购物车的整体价格。
相应代码:
public record CartRow(Product product, int quantity) { // 1
public CartRow(Map.Entry<Product, Integer> entry) {
this(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
public BigDecimal getRowPrice() {
return product.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(quantity));
}
}
var rows = cart.getProducts()
.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(CartRow::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList()); // 1
var price = cart.getProducts()
.entrySet()
.stream()
.map(CartRow::new)
.map(CartRow::getRowPrice) // 2
.reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add); // 3
|
Java流的主要限制之一是只能使用一次。原因是流对象不一定是不变的(尽管它们可以是不变的)。因此,两次执行相同的流可能不是幂等的。
因此,要获取行和价格,我们需要从购物车创建两个流。从一个流中,我们将获得行,而从另一流中,将获得价格。
如果我们想从单个流中收集行和价格。我们需要一个可Collector在一次通过中将两个对象都作为单个对象返回的自定义。
public class PriceAndRows {
private BigDecimal price; // 1
private final List<CartRow> rows = new ArrayList<>(); // 2
PriceAndRows(BigDecimal price, List<CartRow> rows) {
this.price = price;
this.rows.addAll(rows);
}
PriceAndRows() {
this(BigDecimal.ZERO, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
|
这是Collector接口的摘要。有关更多详细信息,请检查此以前的帖子。
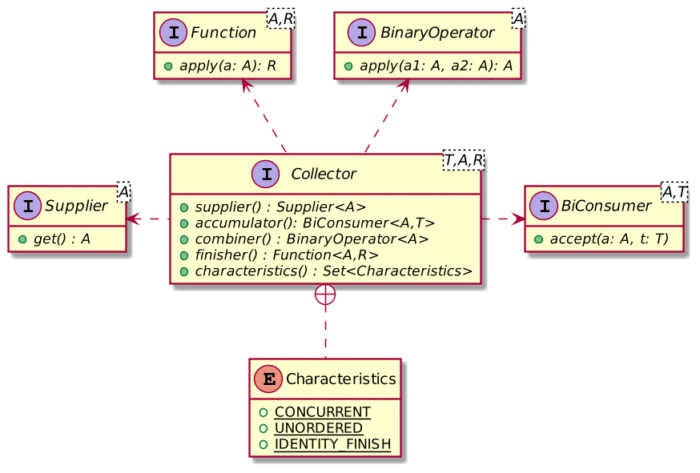
- supplier() 提供基础对象以开始
- accumulator() 描述如何将当前流式项目累积到容器中
- combiner() 如果流是并行的,请描述如何合并它们
- finisher() 如果可变容器类型不是返回的类型,请描述如何将前者转换为后者
- characteristics() 提供元数据以优化流
鉴于此,我们可以相应地实现Collector:
private static class PriceAndRowsCollector
implements Collector<Map.Entry<Product, Integer>, PriceAndRows, PriceAndRows> {
@Override
public Supplier<PriceAndRows> supplier() {
return PriceAndRows::new; // 1
}
@Override
public BiConsumer<PriceAndRows, Map.Entry<Product, Integer>> accumulator() {
return (priceAndRows, entry) -> { // 2
var row = new CartRow(entry);
priceAndRows.price = priceAndRows.price.add(row.getRowPrice());
priceAndRows.rows.add(row);
};
}
@Override
public BinaryOperator<PriceAndRows> combiner() {
return (c1, c2) -> { // 3
c1.price = c1.price.add(c2.price);
var rows = new ArrayList<>(c1.rows);
rows.addAll(c2.rows);
return new PriceAndRows(c1.price, rows);
};
}
@Override
public Function<PriceAndRows, PriceAndRows> finisher() {
return Function.identity(); // 4
}
@Override
public Set<Characteristics> characteristics() {
return Set.of(Characteristics.IDENTITY_FINISH); // 4
}
}
|
设计Collector涉及一些工作,但是使用自定义收集器很容易:
var priceAndRows = cart.getProducts()
.entrySet()
.stream()
.collect(new PriceAndRowsCollector());
|
您可以使用Collectors该类中提供的即用型收集器来解决大多数用例。但是,有些需要实现自定义Collector,例如,当您需要收集多个单个集合或单个标量时,则需要实现一个custom 。
如果您以前从未开发过它,可能看起来很复杂,但事实并非如此。您只需要一点练习即可。希望这篇文章对您有所帮助。
您可以在GitHub上以Maven格式找到此帖子的源代码。

